The origins of oriental carpets
Here you will find information on the history and cultural significance of our oriental carpets.
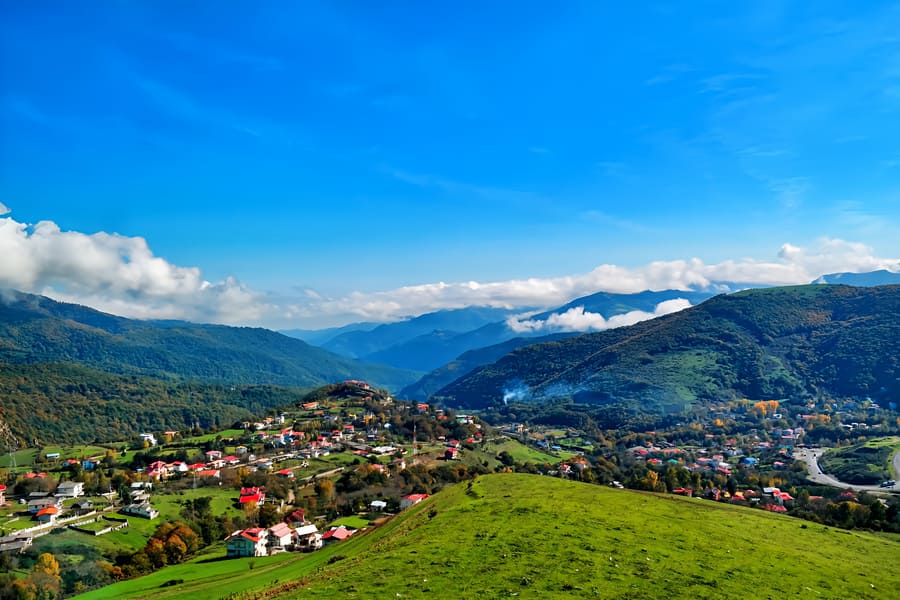

Ardebil
During the Achaemenid period, Ardebil was a strategically important centre in the Persian Empire, playing a role in the trade routes and the regional economy. Under the Parthians and Sassanids, the city retained its importance as a trading centre known for agricultural products. Even in the modern era, Ardebil remained an important centre, developing in areas such as education and business. The history of Ardebil reflects diverse influences from different civilisations and dynasties, and the city has retained its historical and cultural significance over the centuries.
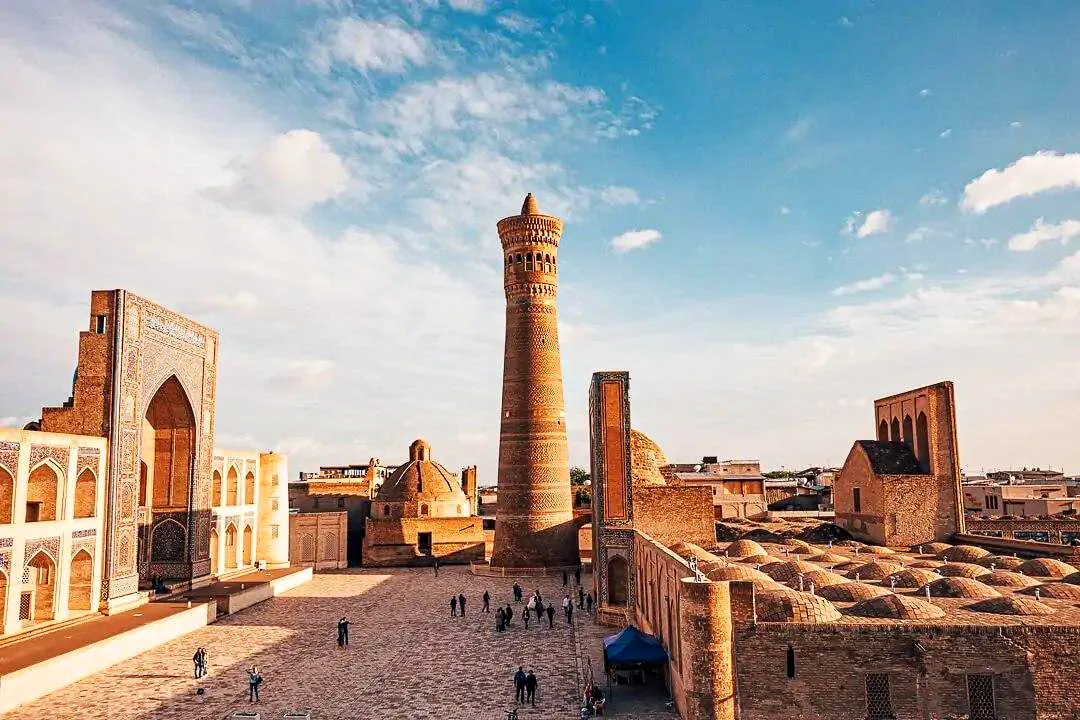

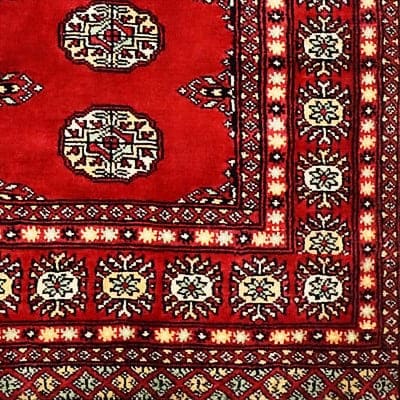
Bukhara
The history of Bukhara, also known as Bukhara, spans more than 2,000 years and includes various civilisations such as the Persians and Greeks. The city gained particular importance as a major trading centre along the Silk Road between East and West. Under the rule of the Abbasi caliphs, Bukhara experienced a heyday of science, literature and art. In the Middle Ages, it was an important centre for trade and the exchange of ideas. After Uzbekistan's independence in the 20th century, Bukhara became part of the new state, but still preserves many historical sites as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Gutshan
Gutshan, a city in north-east Iran, has a long history dating back to prehistoric times. As an important trading hub along the routes between Central Asia, the Caucasus and Iran, the city has historically been characterised by cultural diversity and economic importance. During the Safavid dynasty, Gutshan experienced a boom and developed into a major trading centre thanks to its advantageous location on trade routes. Even in the modern era, the city has maintained its role as an economic centre in various sectors, including agriculture and trade.
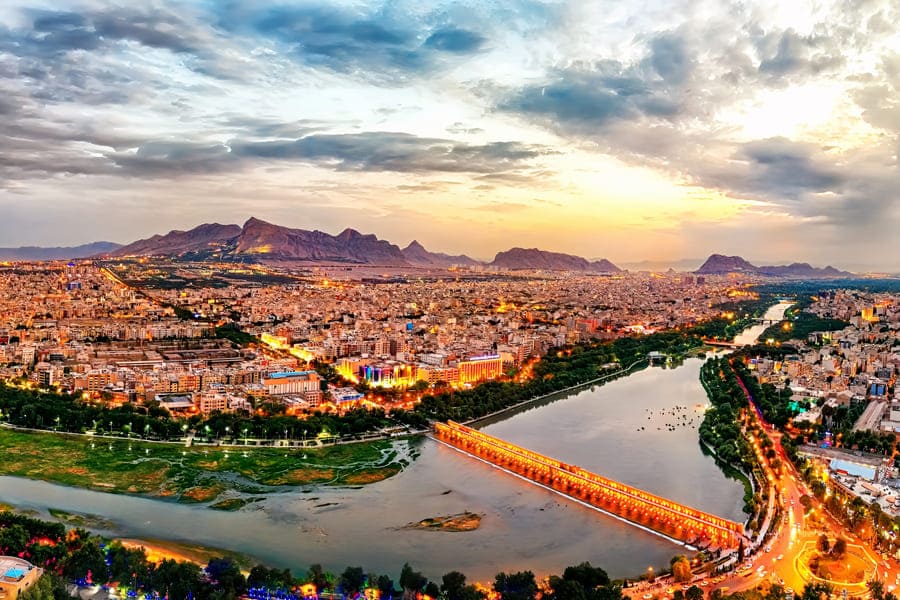

Isfahan
Isfahan, also known as Esfahan, is one of the oldest and most historic cities in Iran. During the Sassanid period, Isfahan retained its importance, with the Sassanids building palaces and the city flourishing due to its strategic location on trade routes. Despite the conquest by Timur and the resulting destruction, Isfahan experienced a phase of restoration and renewal under Timurid rule. The city has played an important role in recent history and is known for its historical monuments such as Imam Square and the Khaju Bridge. It remains a central site in Iran's cultural and historical heritage.

Kashmir
Kashmir, a culturally and historically rich region in northern India, was a centre of Hinduism and Buddhism, shaped by kingdoms such as the Maurya Empire in the 3rd century B.C. In the Middle Ages, Kashmir flourished as a centre of art, literature and science under Hindu rule. Later, the region was influenced by the Mughals. In the 19th century, Kashmir came under the control of the Sikhs under Maharaja Ranjit Singh. When India was partitioned in 1947, the Maharaja joined India, which led to ongoing tensions with Pakistan, which claims part of the region. Kashmir's history is characterised by cultural diversity and political change, which has contributed to ongoing challenges and tensions in the region.

Kazak
The term "Kazak" in the context of the Caucasus refers to various groups and cultural identities, including the Kazakhs, native to Central Asia, as well as ethnic groups in the Caucasus such as the Kists and Kumyks. In the 15th century, the Kazakh people formed an independent political entity, the Kazakh Khanate, which played an important role in the trade routes of the Silk Road. During the 19th century, the Kazakhs increasingly came under Russian influence, which led to drastic political and cultural changes. After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Kazakhs gained their independence and have since developed into an independent nation with a developing economy and culture.

Kashan
The region around Kashan was already inhabited in prehistoric times, with archaeological finds dating back to the 6th millennium BC. During the Parthian and Sassanid periods, Kashan remained an important trading centre, known for textile production and ceramics. During the Seljuk and Ilkhanid eras, Kashan developed into an outstanding centre for trade and crafts in the following centuries. The city's ancient history is characterised by its diverse cultural, craft and economic developments. Over the centuries, Kashan has retained its importance as a cultural and economic centre in Iran.

Kilim Afghan
The tradition of kilims in Afghanistan has a centuries-old history and is firmly rooted in Afghan culture and art. The production of these carpets is closely linked to the nomadic lifestyles of various ethnic groups in the country, including the Pashtuns and Turkmen in particular. These carpets are not only an expression of craftsmanship and creativity, but also of the cultural encounters and historical developments that have characterised the Afghan people. They play an important role in preserving and passing on cultural identity across generations.
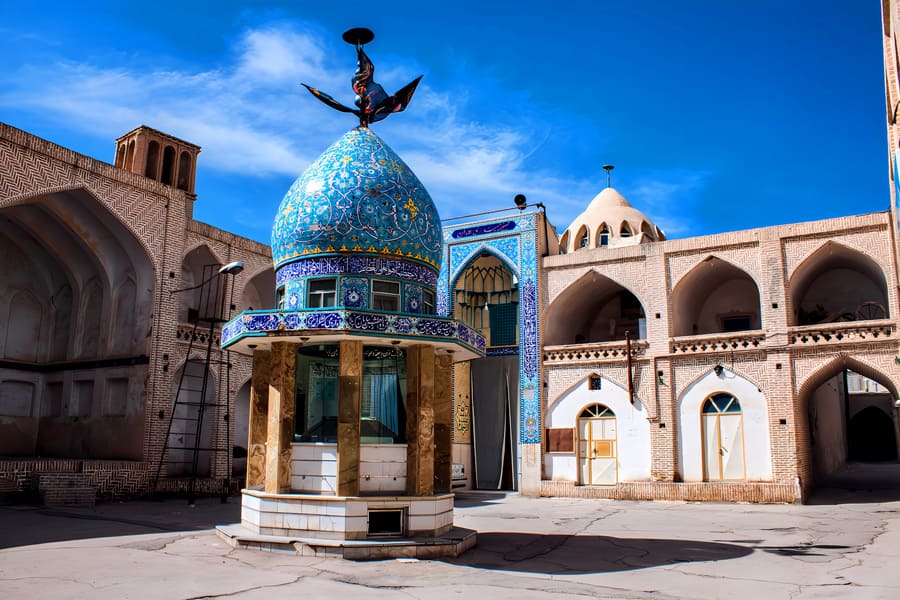

Nain
Nain, also known as Na'in, is a city in central Iran with a rich historical past. During the Achaemenid period, the region was part of the Persian Empire and it is believed that Nain was both a settlement and a potential trading centre. The area was known for its remarkable textile production. Nowadays, Nain is best known for its hand-knotted carpets and traditional architecture. The city has preserved its rich historical heritage and has developed into an important centre for craftsmanship and history.
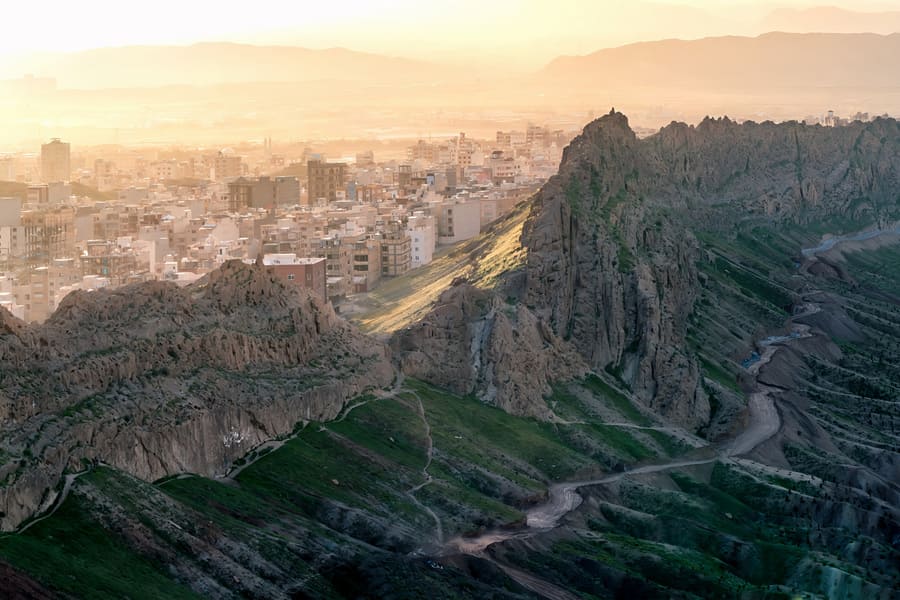

Qum
Qum is a city in Iran with a history dating back to the first millennium BC. Influenced by various civilisations, including the Persians and Medes, Qum was possibly part of the Persian Empire under the Achaemenid dynasty. The city benefited from cultural and economic developments under King Cyrus II. In the following centuries, Qom experienced Parthian and Sassanid rule, which led to intense cultural and political activity in the Persian Empire. In recent decades, Qum has developed considerably and is now one of the largest cities in Iran.
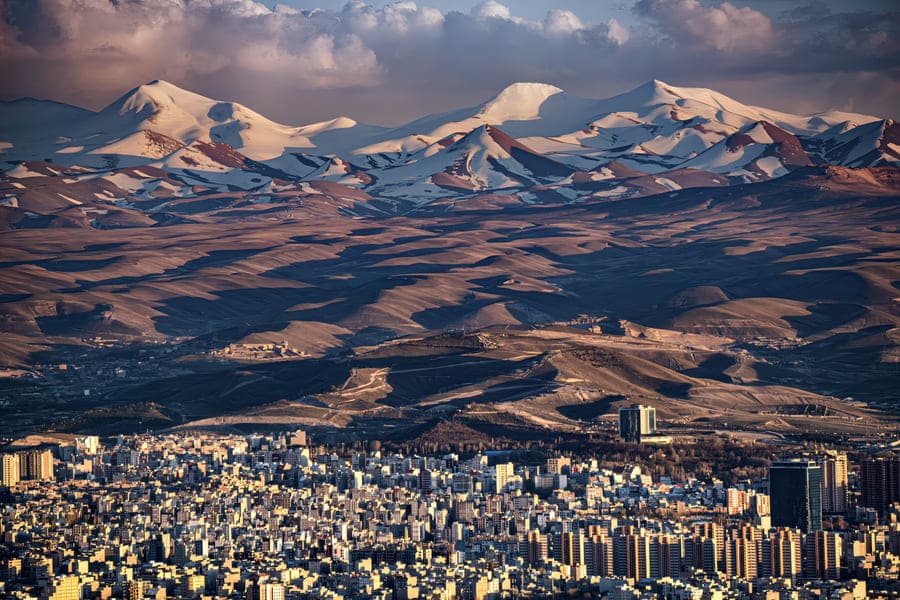

Tabriz
Tabriz, also known as Tabris, is an important city in the north-west of Iran with a rich history dating back to ancient times. During the Parthian and Sassanid era, Tabriz retained its importance as a central trading centre and hub on the trade routes between East and West. In the 13th and 14th centuries, the city came under Mongol and later Timurid rule, but experienced a period of cultural and economic prosperity during the Ilkhanid and Timurid khanates. Tabriz has absorbed various cultural influences over the centuries and retains its strategic and economic importance to this day.

Ziegler
The origins of Ziegler carpets date back to the late 19th century in Iran, particularly in the Sultanabad region (now Arak). Sir Sultan Mahomed Shah, also known as Aga Khan III, initiated this unique carpet style. Under his direction, European designers, including the renowned Swiss company Ziegler & Co, were commissioned to create oriental carpets with western designs. Traditional Persian handicraft techniques were used, but with adaptations to suit European tastes. This creative collaboration resulted in a fascinating fusion of oriental and western aesthetics. The result of this fusion is carpets that not only preserve the elegance of oriental carpet art, but also bridge the gap between the artistic traditions of the East and the West.